
The Ultimate Guide to Trading Gold in Forex
What does trading gold in forex mean?
In forex, you are not buying physical gold; instead, you trade its price through trading platforms.
In other words, you profit from the difference between the buy and sell price, just like regular currency trading.
Many investors look to gold trading in the forex market as a way to hedge against risks and generate profits in uncertain economic environments.
Gold, symbolized by XAU, is one of the most traded assets in the Forex and CFDs markets, attracting both short-term traders and long-term investors.
This guide covers the basics, trading mechanisms, key market drivers, strategies, and practical safety tips.
1. Introduction to Gold Trading in Forex
Unlike purchasing physical gold, trading gold in forex is based on speculation on price movements using financial instruments such as Contracts for Difference (CFDs), giving you the opportunity to profit from rising or falling prices without owning the metal.
Common symbol: Gold versus the US dollar is written as XAU/USD.
The trading mechanism works like any currency pair:
Buying means taking a long position on gold against the dollar.
Selling means taking a short position (selling gold and buying the dollar).
2. How Gold Trading Works
Gold can be traded through several instruments, mainly:
- CFDs: Leverage-based contracts that allow trading with a small margin and gaining from both rising and falling markets, but also increase losses.
- Spot trading: Buying and selling gold at the current price with settlement within two business days.
- Futures: Contracts to exchange gold at a specific price on a future date.
- ETFs: Such as “SPDR Gold Shares (GLD),” providing indirect exposure.
Leverage is a key feature, allowing you to control large positions with limited capital, but it increases risk.
Most platforms charge a spread between the buy and sell price, which is the main trading cost.
3. Key Factors Affecting Gold Prices
Gold prices are driven by several major forces:
- US Dollar Strength: Typically shows an inverse relationship, When the dollar weakens, gold prices tend to rise, making gold cheaper for holders of other currencies.
- Global Economic Uncertainty: During recessions, geopolitical tensions, or crises (such as COVID-19 or wars), investors seek gold as a safe haven.
- Interest Rates & Central Banks: Higher interest rates make yield-bearing assets more attractive than gold, which has no yield.
- Inflation: Gold is a traditional hedge against inflation, so demand rises during periods of rising prices.
- Physical Supply and Demand: Jewelry demand (especially from China and India), along with mining and production activities, influences prices.
Gold is more volatile than traditional currency pairs, and economic news can cause sharp moves within minutes.
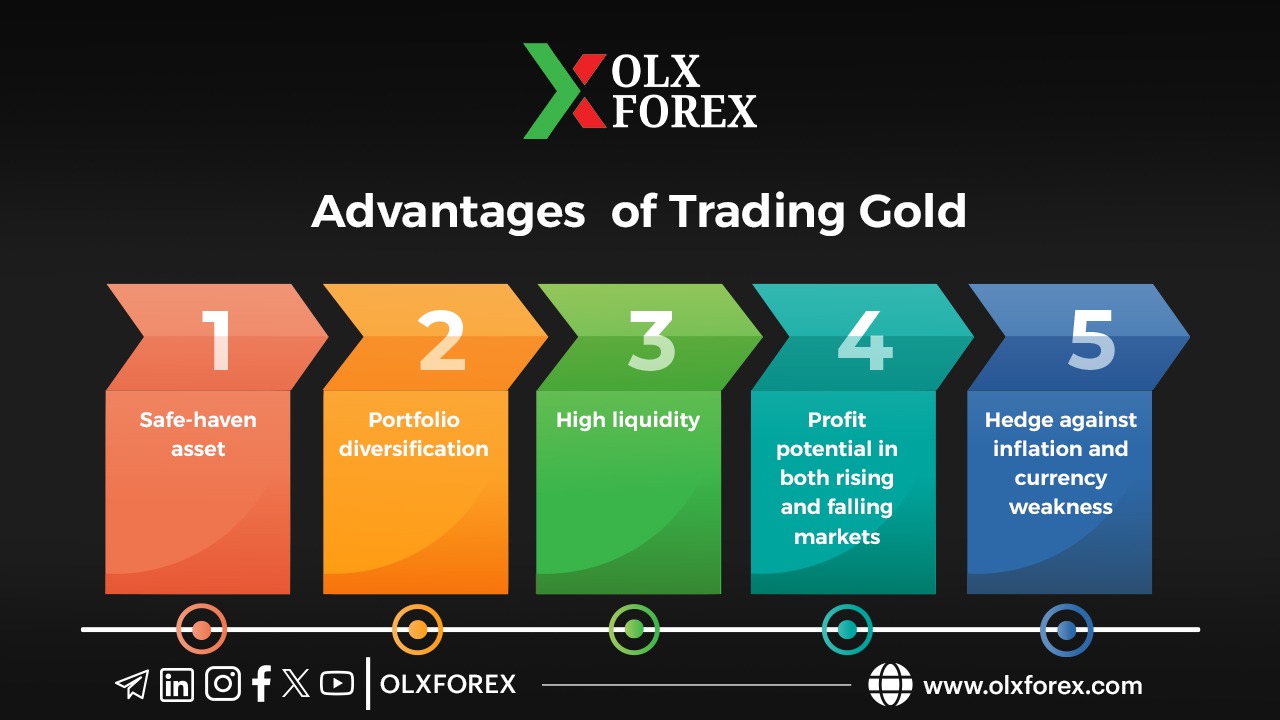
4- Advantages and Disadvantages of Gold
First, the Advantages of Gold
- Safe Haven: Due to its historical value.
- Bank Note: It helps reduce the number of transactions because of its established correlation with other assets such as stocks.
- Consequently: Transactions can be entered and exited easily, allowing for large volumes.
- Opportunities in All Directions: Profit can be made from diversification and short selling.
- Hedging Against Inflation and Currency Weakness
Second, the Disadvantages and Risks
- Multiplier: This can be useful for quick profits.
- Leverage: You can increase capital from investors.
- No Periodic Return: Unlike stocks, which pay a price, gold does not generate returns.
- Complexity in Analysis: It is heavily influenced by intertwined economic and geopolitical factors.
- Usage Costs: Such as spreads and overnight fees.
5- Gold Trading and Advanced Trading
* Fundamental Analysis: Studying influential economic factors such as US data, strategic and strategic factors, the strength of the dollar, and geopolitical influences.
* Technical Analysis: Uses chart indicators and entry and exit points. Common indicators include:
* Animated charts (such as 50-day and 200-day charts) for the year.
* Relative Strength Index (RSI) to identify overbought or oversold conditions.
* Key support and resistance levels.
* News Trading: Investing in the market's reaction to important economic data releases or policy speeches.
* Diversification (Position Diversification): Holding positions for extended periods to adjust or diversify the market, anticipating daily fluctuations.
6 Steps to Getting Started
- Education: Understand the fundamentals of the Forex market, gold trading, and the associated risks.
- Localization Plan: Set specific targets, multiple levels, an entry and exit strategy, and consistently place stop-loss and take-profit orders.
- Choosing a Reliable Broker: Ensure the broker is licensed and regulated by reputable regulatory bodies. Compare spreads, charts, leverage, and platform availability.
- Opening a new account: Companies often start by opening a demo account for practice with virtual capital, then transition to a live account.
- Open a live account with a reputable and licensed company using the following link:
- Start trading with caution: Be aware of the small size of the emerging market, regulatory authorities, and strict adherence to capital management (as a rule, do not risk more than 1-2% of your capital on a single trade).
7- Diversified management in gold
- Use a stop-loss order: This is essential to mitigate risk in a volatile market.
- Completely avoid using leverage: Leverage is a double-edged sword and must be used judiciously to manage multiple trades.
- Bank advice: Do not invest all your capital solely in gold trading.
- Brazilian discipline: Do not allow greed or fear to dictate your actions; stick to your established strategy.
8- Conclusion and final advice
Gold trading in Forex initially presents an opportunity due to its liquidity and safe-haven nature, but over time, the potential risks become higher due to volatility and leverage.
Success in this field depends on consistent funding, meticulous planning, and a multifaceted approach.
Start with a consistent or structured account, and never trade with your own money or risk losing it.
Therefore, people lose money when trading CFDs, and dealing with them requires a deep understanding of the risks involved.











